Click a column header, such as Name, to sort the table by that item.
SEENotes at the bottom of the Table.
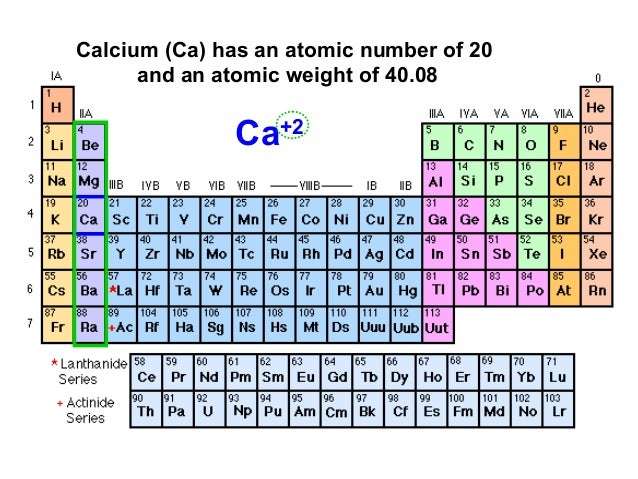
- Calcium, a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20, is a reactive metal that can form a dark oxide-nitrite layer when exposed to the atmosphere.It is the third most abundant metal on the earth's surface after iron and aluminum.
- Calcium The chemical element Calcium (Ca), atomic number 20, is the fifth element and the third most abundant metal in the earth’s crust. The metal is trimorphic, harder than sodium, but softer than aluminium. A well as berylliumand aluminium, and unlike the alkaline metals, it doesn’t cause skin-burns.
| No. | Atomic weight | Name | Sym. | M.P. (°C) | B.P. (°C) | Density* (g/cm3) | Earth crust (%)* | Discovery (Year) | Group* | Electron configuration | Ionization energy (eV) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.008 | Hydrogen | H | -259 | -253 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 1776 | 1 | 1s1 | 13.60 | |
| 2 | 4.003 | Helium | He | -272 | -269 | 0.18 | 1895 | 18 | 1s2 | 24.59 | ||
| 3 | 6.941 | Lithium | Li | 180 | 1,347 | 0.53 | 1817 | 1 | [He] 2s1 | 5.39 | ||
| 4 | 9.012 | Beryllium | Be | 1,278 | 2,970 | 1.85 | 1797 | 2 | [He] 2s2 | 9.32 | ||
| 5 | 10.811 | Boron | B | 2,300 | 2,550 | 2.34 | 1808 | 13 | [He] 2s2 2p1 | 8.30 | ||
| 6 | 12.011 | Carbon | C | 3,500 | 4,827 | 2.26 | 0.09 | ancient | 14 | [He] 2s2 2p2 | 11.26 | |
| 7 | 14.007 | Nitrogen | N | -210 | -196 | 1.25 | 1772 | 15 | [He] 2s2 2p3 | 14.53 | ||
| 8 | 15.999 | Oxygen | O | -218 | -183 | 1.43 | 46.71 | 1774 | 16 | [He] 2s2 2p4 | 13.62 | |
| 9 | 18.998 | Fluorine | F | -220 | -188 | 1.70 | 0.03 | 1886 | 17 | [He] 2s2 2p5 | 17.42 | |
| 10 | 20.180 | Neon | Ne | -249 | -246 | 0.90 | 1898 | 18 | [He] 2s2 2p6 | 21.56 | ||
| 11 | 22.990 | Sodium | Na | 98 | 883 | 0.97 | 2.75 | 1807 | 1 | [Ne] 3s1 | 5.14 | |
| 12 | 24.305 | Magnesium | Mg | 639 | 1,090 | 1.74 | 2.08 | 1755 | 2 | [Ne] 3s2 | 7.65 | |
| 13 | 26.982 | Aluminum | Al | 660 | 2,467 | 2.70 | 8.07 | 1825 | 13 | [Ne] 3s2 3p1 | 5.99 | |
| 14 | 28.086 | Silicon | Si | 1,410 | 2,355 | 2.33 | 27.69 | 1824 | 14 | [Ne] 3s2 3p2 | 8.15 | |
| 15 | 30.974 | Phosphorus | P | 44 | 280 | 1.82 | 0.13 | 1669 | 15 | [Ne] 3s2 3p3 | 10.49 | |
| 16 | 32.065 | Sulfur | S | 113 | 445 | 2.07 | 0.05 | ancient | 16 | [Ne] 3s2 3p4 | 10.36 | |
| 17 | 35.453 | Chlorine | Cl | -101 | -35 | 3.21 | 0.05 | 1774 | 17 | [Ne] 3s2 3p5 | 12.97 | |
| 18 | 39.948 | Argon | Ar | -189 | -186 | 1.78 | 1894 | 18 | [Ne] 3s2 3p6 | 15.76 | ||
| 19 | 39.098 | Potassium | K | 64 | 774 | 0.86 | 2.58 | 1807 | 1 | [Ar] 4s1 | 4.34 | |
| 20 | 40.078 | Calcium | Ca | 839 | 1,484 | 1.55 | 3.65 | 1808 | 2 | [Ar] 4s2 | 6.11 | |
| 21 | 44.956 | Scandium | Sc | 1,539 | 2,832 | 2.99 | 1879 | 3 | [Ar] 3d1 4s2 | 6.56 | ||
| 22 | 47.867 | Titanium | Ti | 1,660 | 3,287 | 4.54 | 0.62 | 1791 | 4 | [Ar] 3d2 4s2 | 6.83 | |
| 23 | 50.942 | Vanadium | V | 1,890 | 3,380 | 6.11 | 1830 | 5 | [Ar] 3d3 4s2 | 6.75 | ||
| 24 | 51.996 | Chromium | Cr | 1,857 | 2,672 | 7.19 | 0.04 | 1797 | 6 | [Ar] 3d5 4s1 | 6.77 | |
| 25 | 54.938 | Manganese | Mn | 1,245 | 1,962 | 7.43 | 0.09 | 1774 | 7 | [Ar] 3d5 4s2 | 7.43 | |
| 26 | 55.845 | Iron | Fe | 1,535 | 2,750 | 7.87 | 5.05 | ancient | 8 | [Ar] 3d6 4s2 | 7.90 | |
| 27 | 58.933 | Cobalt | Co | 1,495 | 2,870 | 8.90 | 1735 | 9 | [Ar] 3d7 4s2 | 7.88 | ||
| 28 | 58.693 | Nickel | Ni | 1,453 | 2,732 | 8.90 | 0.02 | 1751 | 10 | [Ar] 3d8 4s2 | 7.64 | |
| 29 | 63.546 | Copper | Cu | 1,083 | 2,567 | 8.96 | ancient | 11 | [Ar] 3d10 4s1 | 7.73 | ||
| 30 | 65.390 | Zinc | Zn | 420 | 907 | 7.13 | ancient | 12 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 | 9.39 | ||
| 31 | 69.723 | Gallium | Ga | 30 | 2,403 | 5.91 | 1875 | 13 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p1 | 6.00 | ||
| 32 | 72.640 | Germanium | Ge | 937 | 2,830 | 5.32 | 1886 | 14 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p2 | 7.90 | ||
| 33 | 74.922 | Arsenic | As | 81 | 613 | 5.72 | ancient | 15 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p3 | 9.79 | ||
| 34 | 78.960 | Selenium | Se | 217 | 685 | 4.79 | 1817 | 16 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p4 | 9.75 | ||
| 35 | 79.904 | Bromine | Br | -7 | 59 | 3.12 | 1826 | 17 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p5 | 11.81 | ||
| 36 | 83.800 | Krypton | Kr | -157 | -153 | 3.75 | 1898 | 18 | [Ar] 3d10 4s2 4p6 | 14.00 | ||
| 37 | 85.468 | Rubidium | Rb | 39 | 688 | 1.63 | 1861 | 1 | [Kr] 5s1 | 4.18 | ||
| 38 | 87.620 | Strontium | Sr | 769 | 1,384 | 2.54 | 1790 | 2 | [Kr] 5s2 | 5.69 | ||
| 39 | 88.906 | Yttrium | Y | 1,523 | 3,337 | 4.47 | 1794 | 3 | [Kr] 4d1 5s2 | 6.22 | ||
| 40 | 91.224 | Zirconium | Zr | 1,852 | 4,377 | 6.51 | 0.03 | 1789 | 4 | [Kr] 4d2 5s2 | 6.63 | |
| 41 | 92.906 | Niobium | Nb | 2,468 | 4,927 | 8.57 | 1801 | 5 | [Kr] 4d4 5s1 | 6.76 | ||
| 42 | 95.940 | Molybdenum | Mo | 2,617 | 4,612 | 10.22 | 1781 | 6 | [Kr] 4d5 5s1 | 7.09 | ||
| 43 | * | 98.000 | Technetium | Tc | 2,200 | 4,877 | 11.50 | 1937 | 7 | [Kr] 4d5 5s2 | 7.28 | |
| 44 | 101.070 | Ruthenium | Ru | 2,250 | 3,900 | 12.37 | 1844 | 8 | [Kr] 4d7 5s1 | 7.36 | ||
| 45 | 102.906 | Rhodium | Rh | 1,966 | 3,727 | 12.41 | 1803 | 9 | [Kr] 4d8 5s1 | 7.46 | ||
| 46 | 106.420 | Palladium | Pd | 1,552 | 2,927 | 12.02 | 1803 | 10 | [Kr] 4d10 | 8.34 | ||
| 47 | 107.868 | Silver | Ag | 962 | 2,212 | 10.50 | ancient | 11 | [Kr] 4d10 5s1 | 7.58 | ||
| 48 | 112.411 | Cadmium | Cd | 321 | 765 | 8.65 | 1817 | 12 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 | 8.99 | ||
| 49 | 114.818 | Indium | In | 157 | 2,000 | 7.31 | 1863 | 13 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p1 | 5.79 | ||
| 50 | 118.710 | Tin | Sn | 232 | 2,270 | 7.31 | ancient | 14 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p2 | 7.34 | ||
| 51 | 121.760 | Antimony | Sb | 630 | 1,750 | 6.68 | ancient | 15 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p3 | 8.61 | ||
| 52 | 127.600 | Tellurium | Te | 449 | 990 | 6.24 | 1783 | 16 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p4 | 9.01 | ||
| 53 | 126.905 | Iodine | I | 114 | 184 | 4.93 | 1811 | 17 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p5 | 10.45 | ||
| 54 | 131.293 | Xenon | Xe | -112 | -108 | 5.90 | 1898 | 18 | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p6 | 12.13 | ||
| 55 | 132.906 | Cesium | Cs | 29 | 678 | 1.87 | 1860 | 1 | [Xe] 6s1 | 3.89 | ||
| 56 | 137.327 | Barium | Ba | 725 | 1,140 | 3.59 | 0.05 | 1808 | 2 | [Xe] 6s2 | 5.21 | |
| 57 | 138.906 | Lanthanum | La | 920 | 3,469 | 6.15 | 1839 | 3 | [Xe] 5d1 6s2 | 5.58 | ||
| 58 | 140.116 | Cerium | Ce | 795 | 3,257 | 6.77 | 1803 | 101 | [Xe] 4f1 5d1 6s2 | 5.54 | ||
| 59 | 140.908 | Praseodymium | Pr | 935 | 3,127 | 6.77 | 1885 | 101 | [Xe] 4f3 6s2 | 5.47 | ||
| 60 | 144.240 | Neodymium | Nd | 1,010 | 3,127 | 7.01 | 1885 | 101 | [Xe] 4f4 6s2 | 5.53 | ||
| 61 | * | 145.000 | Promethium | Pm | 1,100 | 3,000 | 7.30 | 1945 | 101 | [Xe] 4f5 6s2 | 5.58 | |
| 62 | 150.360 | Samarium | Sm | 1,072 | 1,900 | 7.52 | 1879 | 101 | [Xe] 4f6 6s2 | 5.64 | ||
| 63 | 151.964 | Europium | Eu | 822 | 1,597 | 5.24 | 1901 | 101 | [Xe] 4f7 6s2 | 5.67 | ||
| 64 | 157.250 | Gadolinium | Gd | 1,311 | 3,233 | 7.90 | 1880 | 101 | [Xe] 4f7 5d1 6s2 | 6.15 | ||
| 65 | 158.925 | Terbium | Tb | 1,360 | 3,041 | 8.23 | 1843 | 101 | [Xe] 4f9 6s2 | 5.86 | ||
| 66 | 162.500 | Dysprosium | Dy | 1,412 | 2,562 | 8.55 | 1886 | 101 | [Xe] 4f10 6s2 | 5.94 | ||
| 67 | 164.930 | Holmium | Ho | 1,470 | 2,720 | 8.80 | 1867 | 101 | [Xe] 4f11 6s2 | 6.02 | ||
| 68 | 167.259 | Erbium | Er | 1,522 | 2,510 | 9.07 | 1842 | 101 | [Xe] 4f12 6s2 | 6.11 | ||
| 69 | 168.934 | Thulium | Tm | 1,545 | 1,727 | 9.32 | 1879 | 101 | [Xe] 4f13 6s2 | 6.18 | ||
| 70 | 173.040 | Ytterbium | Yb | 824 | 1,466 | 6.90 | 1878 | 101 | [Xe] 4f14 6s2 | 6.25 | ||
| 71 | 174.967 | Lutetium | Lu | 1,656 | 3,315 | 9.84 | 1907 | 101 | [Xe] 4f14 5d1 6s2 | 5.43 | ||
| 72 | 178.490 | Hafnium | Hf | 2,150 | 5,400 | 13.31 | 1923 | 4 | [Xe] 4f14 5d2 6s2 | 6.83 | ||
| 73 | 180.948 | Tantalum | Ta | 2,996 | 5,425 | 16.65 | 1802 | 5 | [Xe] 4f14 5d3 6s2 | 7.55 | ||
| 74 | 183.840 | Tungsten | W | 3,410 | 5,660 | 19.35 | 1783 | 6 | [Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2 | 7.86 | ||
| 75 | 186.207 | Rhenium | Re | 3,180 | 5,627 | 21.04 | 1925 | 7 | [Xe] 4f14 5d5 6s2 | 7.83 | ||
| 76 | 190.230 | Osmium | Os | 3,045 | 5,027 | 22.60 | 1803 | 8 | [Xe] 4f14 5d6 6s2 | 8.44 | ||
| 77 | 192.217 | Iridium | Ir | 2,410 | 4,527 | 22.40 | 1803 | 9 | [Xe] 4f14 5d7 6s2 | 8.97 | ||
| 78 | 195.078 | Platinum | Pt | 1,772 | 3,827 | 21.45 | 1735 | 10 | [Xe] 4f14 5d9 6s1 | 8.96 | ||
| 79 | 196.967 | Gold | Au | 1,064 | 2,807 | 19.32 | ancient | 11 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s1 | 9.23 | ||
| 80 | 200.590 | Mercury | Hg | -39 | 357 | 13.55 | ancient | 12 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 | 10.44 | ||
| 81 | 204.383 | Thallium | Tl | 303 | 1,457 | 11.85 | 1861 | 13 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p1 | 6.11 | ||
| 82 | 207.200 | Lead | Pb | 327 | 1,740 | 11.35 | ancient | 14 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p2 | 7.42 | ||
| 83 | 208.980 | Bismuth | Bi | 271 | 1,560 | 9.75 | ancient | 15 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p3 | 7.29 | ||
| 84 | * | 209.000 | Polonium | Po | 254 | 962 | 9.30 | 1898 | 16 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p4 | 8.42 | |
| 85 | * | 210.000 | Astatine | At | 302 | 337 | 0.00 | 1940 | 17 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p5 | 9.30 | |
| 86 | * | 222.000 | Radon | Rn | -71 | -62 | 9.73 | 1900 | 18 | [Xe] 4f14 5d10 6s2 6p6 | 10.75 | |
| 87 | * | 223.000 | Francium | Fr | 27 | 677 | 0.00 | 1939 | 1 | [Rn] 7s1 | 4.07 | |
| 88 | * | 226.000 | Radium | Ra | 700 | 1,737 | 5.50 | 1898 | 2 | [Rn] 7s2 | 5.28 | |
| 89 | * | 227.000 | Actinium | Ac | 1,050 | 3,200 | 10.07 | 1899 | 3 | [Rn] 6d1 7s2 | 5.17 | |
| 90 | 232.038 | Thorium | Th | 1,750 | 4,790 | 11.72 | 1829 | 102 | [Rn] 6d2 7s2 | 6.31 | ||
| 91 | 231.036 | Protactinium | Pa | 1,568 | 0 | 15.40 | 1913 | 102 | [Rn] 5f2 6d1 7s2 | 5.89 | ||
| 92 | 238.029 | Uranium | U | 1,132 | 3,818 | 18.95 | 1789 | 102 | [Rn] 5f3 6d1 7s2 | 6.19 | ||
| 93 | * | 237.000 | Neptunium | Np | 640 | 3,902 | 20.20 | 1940 | 102 | [Rn] 5f4 6d1 7s2 | 6.27 | |
| 94 | * | 244.000 | Plutonium | Pu | 640 | 3,235 | 19.84 | 1940 | 102 | [Rn] 5f6 7s2 | 6.03 | |
| 95 | * | 243.000 | Americium | Am | 994 | 2,607 | 13.67 | 1944 | 102 | [Rn] 5f7 7s2 | 5.97 | |
| 96 | * | 247.000 | Curium | Cm | 1,340 | 0 | 13.50 | 1944 | 102 | 5.99 | ||
| 97 | * | 247.000 | Berkelium | Bk | 986 | 0 | 14.78 | 1949 | 102 | 6.20 | ||
| 98 | * | 251.000 | Californium | Cf | 900 | 0 | 15.10 | 1950 | 102 | 6.28 | ||
| 99 | * | 252.000 | Einsteinium | Es | 860 | 0 | 0.00 | 1952 | 102 | 6.42 | ||
| 100 | * | 257.000 | Fermium | Fm | 1,527 | 0 | 0.00 | 1952 | 102 | 6.50 | ||
| 101 | * | 258.000 | Mendelevium | Md | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1955 | 102 | 6.58 | ||
| 102 | * | 259.000 | Nobelium | No | 827 | 0 | 0.00 | 1958 | 102 | 6.65 | ||
| 103 | * | 262.000 | Lawrencium | Lr | 1,627 | 0 | 0.00 | 1961 | 102 | 4.90 | ||
| 104 | * | 261.000 | Rutherfordium | Rf | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1964 | 4 | 0.00 | ||
| 105 | * | 262.000 | Dubnium | Db | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1967 | 5 | 0.00 | ||
| 106 | * | 266.000 | Seaborgium | Sg | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1974 | 6 | 0.00 | ||
| 107 | * | 264.000 | Bohrium | Bh | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1981 | 7 | 0.00 | ||
| 108 | * | 277.000 | Hassium | Hs | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1984 | 8 | 0.00 | ||
| 109 | * | 268.000 | Meitnerium | Mt | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 1982 | 9 | 0.00 | ||
| No. | Atomic weight | Name | Sym. | M.P. (°C) | B.P. (°C) | Density* (g/cm3) | Earth crust (%)* | Discovery (Year) | Group* | Electron configuration | Ionization energy (eV) |
Notes:
• Density of elements with boiling points below 0°C is given in g/l. In a sorted list, these elements are shown before other elements that have boiling points >0°C.
• Earth crust composition average values are from a report by F. W. Clarke and H. S. Washington, 1924. Elemental composition of crustal rocks differ between different localities (see article).
• Group: There are only 18 groups in the periodic table that constitute the columns of the table. Lanthanoids and Actinoids are numbered as 101 and 102 to separate them in sorting by group.
• The elements marked with an asterisk (in the 2nd column) have no stable nuclides. For these elements the weight value shown represents the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element.
Abbreviations and Definitions:
The number of protons of a neutral atom and its ion is the same. 40 Ca and 40 Ca 2+ both have 20 protons. 40 Ca has 20 electrons. 40 Ca 2+ has 18 electrons. The +2 charge on 40 Ca 2+ indicates that 40 Ca 2+ has 2 less electrons than 40 Ca. 35 Cl-and 40 Ca 2+ have the same number of electrons.
No. - Atomic Number; M.P. - melting point; B.P. - boiling point
Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom. Each element is uniquely defined by its atomic number.

Atomic mass: The mass of an atom is primarily determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Atomic mass is measured in Atomic Mass Units (amu) which are scaled relative to carbon, 12C, that is taken as a standard element with an atomic mass of 12. This isotope of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Thus, each proton and neutron has a mass of about 1 amu.
Isotope: Atoms of the same element with the same atomic number, but different number of neutrons. Isotope of an element is defined by the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Elements have more than one isotope with varying numbers of neutrons. For example, there are two common isotopes of carbon, 12C and 13C which have 6 and 7 neutrons respectively. The abundances of different isotopes of elements vary in nature depending on the source of materials. For relative abundances of isotopes in nature see reference on Atomic Weights and Isotopic Compositions.
Ca Atomic Number Of Protons And Electrons
Atomic weight: Atomic weight values represent weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. The values shown here are based on the IUPAC Commission determinations (Pure Appl. Chem. 73:667-683, 2001). The elements marked with an asterisk have no stable nuclides. For these elements the weight value shown represents the mass number of the longest-lived isotope of the element.
Electron configuration: See next page for explanation of electron configuration of atoms.
Ionization energy (IE): The energy required to remove the outermost electron from an atom or a positive ion in its ground level. The table lists only the first IE in eV units. To convert to kJ/mol multiply by 96.4869. Reference: NIST Reference Table on Ground states and ionization energies for the neutral atoms. IE decreases going down a column of the periodic table, and increases from left to right in a row. Thus, alkali metals have the lowest IE in a period and Rare gases have the highest.
Other resources related to the Periodic Table
- Chemical Evolution of the Universe
We remember from our school chemistry course that every element has its own specific atomic number. It is the same as the number of protons that the atom of each element has, so sometimes atomic number is called proton number. It is always the whole number and it ranges from 1 to 118, according to the number of the element in the Periodic Table. This number can be really important and something essential to know, in relation to a certain chemical element which is the issue of our interest at the moment.

Why is this so? Why is the atomic number so important? First of all, it is the number that makes elements different from one another as it shows the number of protons in their nuclei. Also, knowing the atomic number of an element can give us an idea about the position of the element in the Periodic Table. Atomic number of an element never changes: for example, the atomic number of oxygen is always 8, and the atomic number of Chlorine is always 18. The atomic number is marked with the symbol Z, taken from a German word zahl (or atomzahl, which is 'atomic number' in German).
This website is created for those who need to know the atomic number of a central chemical element. By using our website, you can do it in just one click and receive short and correct information on this matter. There is also some extra summary on every each chemical element which can be found at our website, including the atomic weight of each element, as well as physical and chemical properties of every element and its importance. Use this website at any time when you need to get fast and precise information about atomic or proton number of chemical elements.
List of chemical elements in periodic table with atomic number, chemical symbol and atomic weight. You can sort the elements by clicking on the table headers. Please click on the element name for complete list of element properties.
| Atomic Number | Chemical Symbol | Element Name | Atomic Weight (u) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | Hydrogen | 1.008 |
| 2 | He | Helium | 4.003 |
| 3 | Li | Lithium | 6.94 |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium | 9.012 |
| 5 | B | Boron | 10.81 |
| 6 | C | Carbon | 12.011 |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen | 14.007 |
| 8 | O | Oxygen | 15.999 |
| 9 | F | Fluorine | 18.998 |
| 10 | Ne | Neon | 20.18 |
| 11 | Na | Sodium | 22.99 |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium | 24.305 |
| 13 | Al | Aluminium | 26.982 |
| 14 | Si | Silicon | 28.085 |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus | 30.974 |
| 16 | S | Sulfur | 32.06 |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine | 35.45 |
| 18 | Ar | Argon | 39.948 |
| 19 | K | Potassium | 39.098 |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium | 40.078 |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | 44.956 |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium | 47.867 |
| 23 | V | Vanadium | 50.942 |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium | 51.996 |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese | 54.938 |
| 26 | Fe | Iron | 55.845 |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt | 58.933 |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel | 58.693 |
| 29 | Cu | Copper | 63.546 |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc | 65.38 |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium | 69.723 |
| 32 | Ge | Germanium | 72.63 |
| 33 | As | Arsenic | 74.922 |
| 34 | Se | Selenium | 78.971 |
| 35 | Br | Bromine | 79.904 |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton | 83.798 |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium | 85.468 |
| 38 | Sr | Strontium | 87.62 |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | 88.906 |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium | 91.224 |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium | 92.906 |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum | 95.95 |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium | 98 |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium | 101.07 |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium | 102.906 |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium | 106.42 |
| 47 | Ag | Silver | 107.868 |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium | 112.414 |
| 49 | In | Indium | 114.818 |
| 50 | Sn | Tin | 118.71 |
| 51 | Sb | Antimony | 121.76 |
| 52 | Te | Tellurium | 127.6 |
| 53 | I | Iodine | 126.904 |
| 54 | Xe | Xenon | 131.293 |
| 55 | Cs | Caesium | 132.905 |
| 56 | Ba | Barium | 137.327 |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum | 138.905 |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium | 140.116 |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium | 140.908 |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium | 144.242 |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium | 145 |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium | 150.36 |
| 63 | Eu | Europium | 151.964 |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium | 157.25 |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium | 158.925 |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium | 162.5 |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium | 164.93 |
| 68 | Er | Erbium | 167.259 |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium | 168.934 |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium | 173.045 |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium | 174.967 |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium | 178.49 |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum | 180.948 |
| 74 | W | Tungsten | 183.84 |
| 75 | Re | Rhenium | 186.207 |
| 76 | Os | Osmium | 190.23 |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium | 192.217 |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum | 195.084 |
| 79 | Au | Gold | 196.967 |
| 80 | Hg | Mercury | 200.592 |
| 81 | Tl | Thallium | 204.38 |
| 82 | Pb | Lead | 207.2 |
| 83 | Bi | Bismuth | 208.98 |
| 84 | Po | Polonium | 209 |
| 85 | At | Astatine | 210 |
| 86 | Rn | Radon | 222 |
| 87 | Fr | Francium | 223 |
| 88 | Ra | Radium | 226 |
| 89 | Ac | Actinium | 227 |
| 90 | Th | Thorium | 232.038 |
| 91 | Pa | Protactinium | 231.036 |
| 92 | U | Uranium | 238.029 |
| 93 | Np | Neptunium | 237 |
| 94 | Pu | Plutonium | 244 |
| 95 | Am | Americium | 243 |
| 96 | Cm | Curium | 247 |
| 97 | Bk | Berkelium | 247 |
| 98 | Cf | Californium | 251 |
| 99 | Es | Einsteinium | 252 |
| 100 | Fm | Fermium | 257 |
| 101 | Md | Mendelevium | 258 |
| 102 | No | Nobelium | 259 |
| 103 | Lr | Lawrencium | 266 |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium | 267 |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium | 268 |
| 106 | Sg | Seaborgium | 269 |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium | 270 |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium | 277 |
| 109 | Mt | Meitnerium | 278 |
| 110 | Ds | Darmstadtium | 281 |
| 111 | Rg | Roentgenium | 282 |
| 112 | Cn | Copernicium | 285 |
| 113 | Nh | Nihonium | 286 |
| 114 | Fl | Flerovium | 289 |
| 115 | Mc | Moscovium | 290 |
| 116 | Lv | Livermorium | 293 |
| 117 | Ts | Tennessine | 294 |
| 118 | Og | Oganesson | 294 |
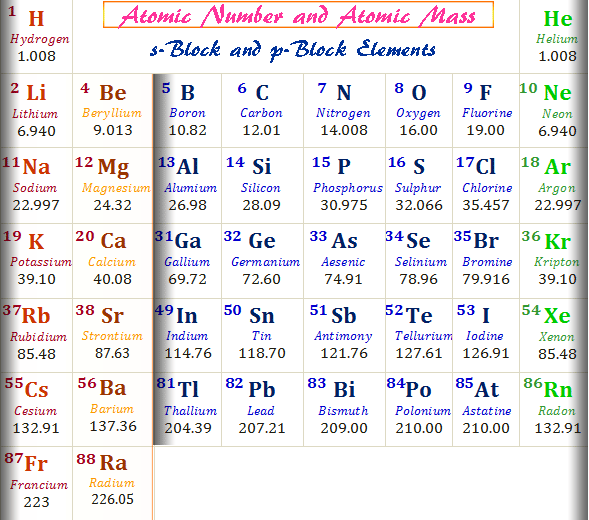
Lists of Elements in Periodic Table
You can also list the elements in various ordered properties with printable tables below.
Ca Atomic Number
Lists of Elements by Group Number in Periodic Table
Calcium Atom
Ca Ka Atomic Number
» Group 1» Group 2» Group 3» Group 4» Group 5» Group 6» Group 7» Group 8» Group 9» Group 10» Group 11» Group 12» Group 13» Group 14» Group 15» Group 16» Group 17» Group 18